Definition – What does Injection Pressure mean?
Injection Pressure is the pressure applied on the injection screw when a material is being injected into the mold. It is useful for the treatment of the rock matrix. Injection Pressure enables test fluids to be injected into rock formations without causing breakdowns or fractures.
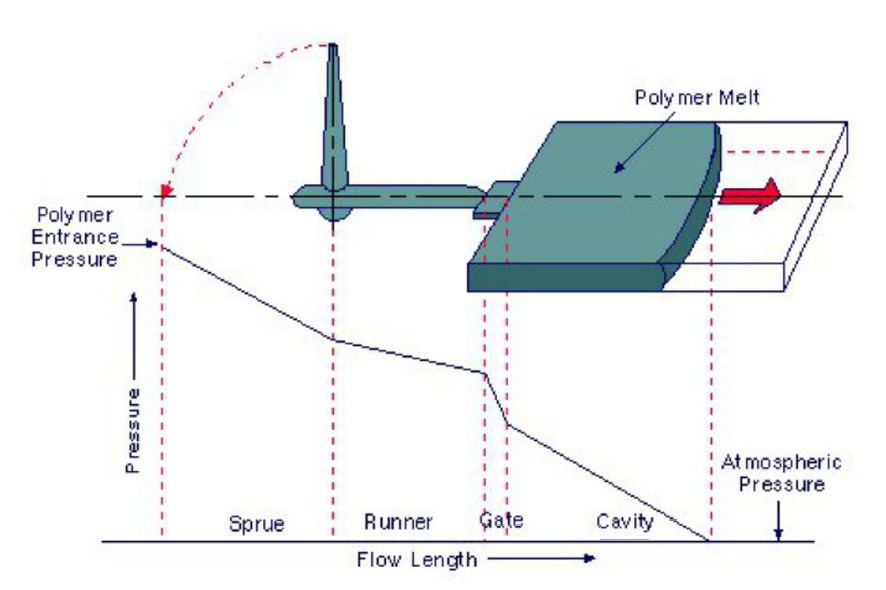
However, it requires surface pump pressure to achieve injection. The hydrostatic pressure of the liquid also affects the pressure injection as it contributes to the downhole pressure value.
Injection Pressure is demonstrated in terms of PSI.
Petropedia explains Injection Pressure
Injection Pressure is used in injection molding machines. As the plastic materials that are used in the devices are quite stiff, they need injection pressure to fill the mold. It is one of the essential factors that are used to determine the properties of molded parts in the machine. The pressure should be high so that it can fill the molten polymer into the mold completely. It is further categorized into two parts, i.e., fill pressure and hold pressure. Fill pressure is stronger as compared to hold pressure.
Setting Tips:
1. It must be smaller the the machine`s max. injection pressure
2. Try to use a lower pressure as possible as you can while testing production
3. Avoid to set it in high speed and high injection pressure at the same time
Injection Pressure Table for Different Plastics:
| Raw Material | Injection Pressure (Mpa) | Raw Material | Injection Pressure (Mpa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASA | 50 ~ 100 | ABS | 50 ~ 100 |
| BDS | 40 ~ 80 | SAN | 35 ~ 130 |
| HIPS | 30 ~ 80 | GPPS | 30 ~ 80 |
| PP | 30 ~ 80 | HDPE | 70 ~ 105 |
| LDPE | 30 ~ 80 | PA6 | 75 ~ 125 |
| PA66 | 75 ~ 125 | PC | 90 ~ 180 |
| PBT | 100 ~ 140 | PEI | 70 ~ 150 |
| PET | 30 ~ 130 | PMMA | 80 ~ 130 |
| POM | 70 ~ 120 | PPS | 60 ~ 140 |
| PSU | 100 ~ 150 | TPU/PUR | 20 ~ 110 |
| PVC | 70 ~ 110 | ABS+PC | 80 ~ 140 |
| *Injection pressure for common plasics | |||
What is Backpressure?
Backpressure is generated at the front end of the screw as the screw is rotated. It causes the heat softened(plasticized) material to be forced along the metering section of the screw and through the non-return(check ring) valve assembly. Because of the build up of material, pressure is created and when it is of sufficient value it will force the rotating screw backwards its metering or dosing stroke position. Therefore, as the rotating screw moves backwards, material enters and increase in volume at the front of the rotating screw, and this filling continoues until the screw reaches its selected stroke position.
Setting Tips:
1. Adjust the backpressure according to the materials properties
2. Adjust the backpressure refering to the products surface quality and the dimensional precision
Backpressure`s Table Sheet for Different Plastics:
| Raw Material | Injection Pressure (Mpa) | Raw Material | Injection Pressure (Mpa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASA | 9.5 ~ 15 | ABS | 9.0 ~ 18 |
| BDS | 3.0 ~ 10 | SAN | 5.0 ~ 15 |
| HIPS | 5.0 ~ 10 | GPPS | 5.0 ~ 10 |
| PP | 9.0 ~ 17 | HDPE | 7.0 ~18 |
| LDPE | 7.0 ~ 18 | PA6 | 2.0 ~ 6.0 |
| PA66 | 2.0 ~ 6.0 | PC | 6.0 ~ 15 |
| PBT | 5.0 ~ 10 | PEI | 5.0 ~ 18 |
| PET | 5.0 ~ 10 | PMMA | 13 ~ 28 |
| POM | 5.0 ~ 10 | PPS | 3.0 ~ 15 |
| PSU | 5.0 ~ 12 | TPU/PUR | 1.0 ~ 5.0 |
| PVC | 4.0 ~ 8.0 | ABS+PC | 5.0 ~ 12 |
| *Injection pressure for common plasics | |||